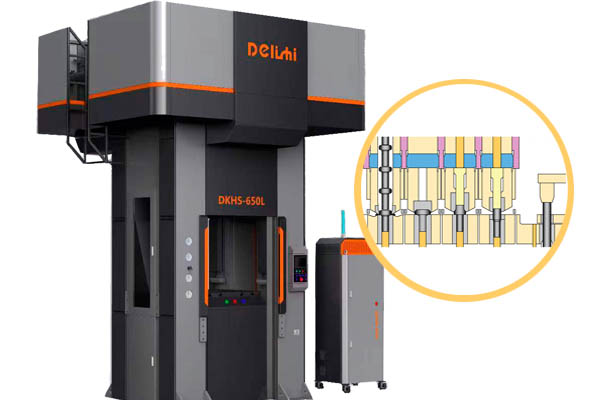
Mold
The mold is one of the most critical tools of cold forging press. It determines the shape and size of the cold forged product. The cold forging mold is generally composed of an upper and lower mold, the upper mold is fixed on the slide of the hydraulic press, and the lower mold is installed on the workbench. The material of the mold needs to have high hardness, high strength and good wear resistance, such as mold steel such as Cr12MoV and H13. According to different product shapes, there are various types of molds, such as punching dies, extrusion dies, upsetting dies, etc. For example, when producing automobile half-axles, a specially designed extrusion die is required to gradually deform the half-axle blank in the mold cavity and finally form it.
Lubricant
Lubricant plays a vital role in the cold forging process. It can reduce the friction between the die and the workpiece, reduce the forging force, and increase the life of the die. Commonly used cold forging lubricants include graphite lubricant, molybdenum disulfide lubricant, etc. Before cold forging, apply the lubricant evenly on the surface of the blank or apply it by spraying. For example, when cold forging nuts, the use of graphite lubricant can make the upsetting process smoother, reduce the wear on the die surface, and also make the nut surface quality better.
Blank shearing device
The blank shearing device is used to cut the raw materials into blanks of suitable size. It can be an independent shearing machine or bar shearing machine, or it can be a part integrated in the cold forging hydraulic press production line. By accurately controlling the shearing force and shearing size, accurate blanks can be provided for cold forging. For example, for a production line producing cold forged bolts, the blank shearing device can shear long round steel bars into bolt blanks of specified length, and its length tolerance can be controlled within ±0.5mm.
Automatic feeding device
The automatic feeding device can realize the automatic conveying of blanks and improve the working efficiency and automation of the cold forging hydraulic press. It can be fed by a robot arm, a conveyor belt or a vibrating plate. The robot arm has high feeding accuracy and is suitable for large and heavy blanks; the conveyor belt feeding is suitable for continuous conveying of regular-shaped blanks; the vibrating plate feeding is mainly used for small and light blanks. For example, in a cold forging workshop that produces small hardware, a vibrating plate can transport a large number of nut blanks to the working area of the cold forging hydraulic press in an orderly manner.
Unloading device
The unloading device is used to remove the product from the mold after cold forging. Common unloading methods include mechanical unloading and pneumatic unloading. The mechanical unloading device pushes the product out of the mold through a mechanical structure, such as a unloading plate, an unloading rod, etc.; pneumatic unloading uses the power of compressed air to blow the product out of the mold. For example, when cold forging some products with complex shapes that are easy to get stuck in the mold, the pneumatic unloading device can quickly and effectively remove the product to ensure the continuity of production.
Hardness testing tools
Hardness testing tools are used to detect the hardness of cold forged products to ensure that the product quality meets the requirements. Common hardness testing methods include Rockwell hardness tester, Brinell hardness tester and Vickers hardness tester. Rockwell hardness tester has a fast detection speed and is suitable for batch detection; Brinell hardness tester is suitable for detecting products with lower hardness and thicker materials; Vickers hardness tester can accurately measure the hardness of a small area. For example, after cold forging high-strength bolts, a Rockwell hardness tester is used to test the hardness of the bolt head to ensure that its hardness is within the specified range to meet the use requirements.
Dimension measuring tools
Dimension measuring tools are essential and are used to check the dimensional accuracy of cold forged products. Calipers, micrometers, plug gauges, etc. are all commonly used dimensional measuring tools. Calipers can measure basic dimensions such as length, width, and thickness of products; micrometers can more accurately measure changes in smaller dimensions; plug gauges are mainly used to measure the size of holes. For example, when cold forging precision gears, micrometers are used to measure the tooth thickness of the gears to ensure that their dimensional tolerances are controlled within a very small range and meet the design standards.
Die installation tools
Die installation tools are used to install and remove cold forging dies. Including tools such as wrenches, bolts, and jacks. When installing the die, tools such as wrenches are needed to tighten the bolts that fix the die to ensure that the die is firmly installed. When the die needs to be replaced, the jack can assist in removing the die from the slide or workbench of the hydraulic press. For example, when replacing the cold forging extrusion die, the old die is lifted up by the jack, and then the fixing bolts are removed with a wrench to complete the die replacement conveniently and quickly.
Pressure sensor
The pressure sensor is installed in the hydraulic system of the cold forging hydraulic press to monitor the forging pressure in real time. Through the pressure sensor, the pressure during the cold forging process can be accurately controlled to avoid damage to the die or product defects caused by excessive pressure. At the same time, it can also ensure that the cold forging is completed under appropriate pressure to ensure product quality. For example, when cold forging large forgings, the pressure sensor can feed back the pressure data to the control system. When the pressure is close to the set maximum value, the control system can adjust the working parameters of the hydraulic press to prevent overload.
Control system terminal
The control system terminal is the "brain" of the cold forging press. It can be a dedicated control cabinet or a computer-based control software. Through the control system terminal, the working parameters of the cold forging hydraulic press, such as pressure, stroke, speed, etc., can be set, and the operating status and fault alarm of the equipment can be monitored. For example, the operator can input the pressure value and stroke length required for cold forging a certain product on the control system terminal, and the hydraulic press will work according to the set parameters. In addition, when the oil temperature is too high or the pressure is abnormal, the control system terminal will promptly issue an alarm.
- Cold Forging Press
Tags :


 +86-13509801050
+86-13509801050
 E-mail
E-mail
